Understanding Order-Driven Markets: Transparency and Risk Management in Action
In modern financial markets, understanding the mechanics of trading systems is essential for effective investment decision-making and financial risk management. One of the most influential systems used today is the order-driven market, a structure that plays a central role in global equity exchanges like Euronext, Nasdaq, and the London Stock Exchange.
What Are Order-Driven Markets?
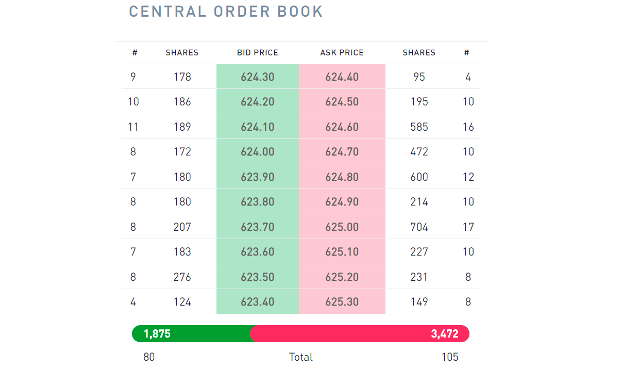
An order-driven market operates through a central order book where buyers and sellers input their orders. Unlike quote-driven markets, where prices are set by market makers, in an order-driven system, prices emerge organically based on supply and demand. This structure enhances market transparency, provides better liquidity risk insights, and empowers participants to implement nuanced trading strategies.
The two most important types of orders in this system are:
-
Market Orders: Executed immediately at the best available price. These orders offer speed but come with market risk due to price uncertainty.
-
Limit Orders: Executed only when a specified price is met, allowing better control over execution price but introducing timing uncertainty.
Amsshare leverages deep knowledge of these mechanisms to build tailored tools for investment funds, UCITS-compliant strategies, and high-volume traders.
Bid-Ask Spread and Market Liquidity
At the heart of the order-driven market lies the bid-ask spread—the difference between the highest bid (buy) and the lowest ask (sell) prices. This spread is a key indicator of market risk and liquidity:
-
A narrow spread reflects a liquid, active market.
-
A wider spread signals illiquidity and higher transaction costs.
Live examples from stocks like ASML Holding NV demonstrate this concept in action, with narrow spreads suggesting high investor activity and minimal price slippage—ideal conditions for effective risk solutions.
Brokers and Trade Execution
In order-driven markets, brokers play a crucial role as facilitators. While they do not act as market makers or hold inventory, brokers submit orders on behalf of clients and ensure trades are executed efficiently. This removes direct interaction between retail investors and the market, streamlining the process but making order flow a key determinant of market depth and liquidity.
Understanding how brokers operate within this structure allows Amsshare to craft AI-driven solutions for clients seeking to improve trade execution and reduce exposure to operational risks.
Advantages of Order-Driven Markets
Order-driven markets offer significant benefits over quote-driven systems:
-
Transparency: All orders are visible in the public order book, improving market risk oversight and promoting fair pricing.
-
Lower Costs: Without the need for market makers, transaction costs are generally lower.
-
Flexibility: A wide array of order types, such as stop-loss or trailing stop orders, provides investors with tools for precision risk management.
These features align perfectly with Amsshare’s mission to deliver custom risk solutions and enhance decision-making across asset classes.
How Amsshare Adds Value
At Amsshare, we understand the real-world frictions—like low liquidity or large-volume trade challenges—that investors face. Our team applies theoretical expertise and practical knowledge to develop tailored tools for:
-
Liquidity risk analysis
-
Market impact assessment
-
AI-enhanced trade optimisation
-
Financial risk modelling
By integrating order book dynamics into your strategic framework, we help you make informed, timely, and cost-effective decisions.